Coming on the shelf soon…
VitaMem:
Cognitive and memory enhancer.
Tablets and powder in sachet for oral use.
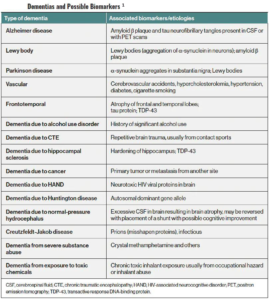
Dementia is a powerful/painful, frightening and life-changing diagnosis that is followed by a trail of sadness, helplessness, grief, and loss. It is a syndrome that may affect many aspects of cognition (Table 1); it typically follows a neurodegenerative course with increased functional impairment and eventual total inability to care for oneself.

Some older adults have more memory or thinking problems than other adults their age. This condition is called mild cognitive impairment, or MCI.
There is no single cause of MCI. The risk of developing MCI increases as someone gets older. Conditions such as diabetes, depression, and stroke may increase a person’s risk for MCI 2.
Researchers have found that more people with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) than those without it go on to develop Alzheimer’s disease or a related dementia. An estimated 10 to 20% of people age 65 or older with MCI develop dementia over a one-year period. However, not everyone who has MCI develops dementia. In many cases, the symptoms of MCI may stay the same or even improve 2.
Agitation associated with Alzheimer disease dementia (AAD) is one of the most difficult complications of dementia. Meanwhile, the need for treatments of Alzheimer disease and dementia remains huge and largely unaddressed 3.
According to an estimate by the WHO, between 2015 and 2050, the share of the world’s population over 60 years is expected to double from 12 to 22 percent. The pace at which the population is aging has increased incrementally worldwide. In addition, human life expectancy has also increased at a rapid rate. India’s senior population has been steadily increasing since 1961 4.
The growth rate of the over 65 demographic in the country has partially been due to reduced death rates as a result of the success of diverse health interventions following the census 1981. People are living longer, and estimates reflect that over 10 percent of the country’s population is over the age of 60 years in 2021 4.
The old-age dependency metric is used to gauge the ratio between the number of persons over the age of 65 years and the number of persons between the ages of 15 and 64 years, expressed per 100 persons. In India, this ratio grew from almost 11 percent to over 14 percent from 1961 to 2011 and was projected to increase to over 20 percent in 2031 4.
The distribution of elderly who are economically dependent on other people saw an increase in the rural areas. However, the proportion of entirely dependent elderly in rural as well as urban areas had declined. In 2017, those that were entirely dependent in rural areas relied on their children or their needs while second in line was the relative spouse 4.
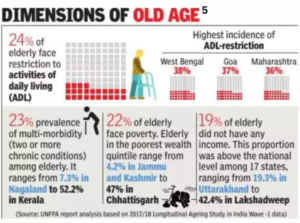
The challenges further pile on from a rising need for healthcare with an increase in age. Due to higher morbidity from chronic diseases, the elderly have long-standing healthcare needs that are tied together with high out-of-pocket expenditures which more than three-fourths of them cannot afford. In order to effectively address these challenges, there is a pressing need of positioning elderly health care into a broader framework 4.
A rough estimate in 2010 pegged the total societal cost of dementia for India to be US$ 3.415 billion (INR 147 billion); with its 56% (INR 88.9 billion) being the informal care costs and 29% being direct medical costs (INR 46.8 billion). Rao and Bharathest imated the annual household cost of caring for a person with dementia in India, depending on the severity of the disease, to range from INR 45,600 to INR 2, 02,450 in urban areas and INR 20,300 to INR 66,025 in rural areas. Costs increased with increasing severity of the disease 5.
Our product is an innovation which aims to address this unmet need both in terms of therapy and cost as well as provide a benefit beyond improving dementia and cognitive impairment.
The other pleiotropic benefits include an aid to enhancement in memory, general health, immunity and benefit as an antioxidant.
The benefits have been described in standard traditional medicine texts for the ingredients.
These are ingredients that are safe to use as has been proven by a millennia of usage.
The costs to the family would be far less compared to what contemporary medicine and supplements have to offer.
The added benefit is addressing the pain point of both the patients and the caregivers in bringing down the cost burden and improving the quality of life of the patient for an economically beneficial cost.
Ancient Indian herbs and systems of medicine are able to address some aspects of the above problem statement to various degrees.
Acknowledgement: The content of this page is acknowledged as the knowledge of references mentioned below. All due credit is given to the authors of the source references.
Adapted from source references:
- John J Miller. 2023. https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/dementia-treatment-an-unmet-need
- National Institutes of Health. 2021. https://shorturl.at/xBsyN
- Leah Kuntz. 2023. https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/fda-approves-first-treatment-for-agitation-associated-with-alzheimer-disease-dementia
- (https://www.statista.com/statistics/1303304/india-old-age-dependency-ratio/)
- Kumar CS, George S, Kallivayalil RA. Towards a Dementia-Friendly India. Indian J Psychol Med. 2019 Sep 5;41(5):476-481. doi: 10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_25_19. PMID: 31548773; PMCID: PMC6753713.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.